The Mystery of the Staff of Moses: Biblical Relic or Ancient Legend?
For millennia, the story of Moses and his staff has captured the imagination of believers, historians, and researchers alike. This seemingly ordinary wooden rod, imbued with miraculous powers according to biblical tradition, is said to have played a pivotal role in liberating the Israelites from Egypt. Today, two claimed relics—one housed in the Topkapi Palace Museum in Turkey and another in the Birmingham Museum in England—fuel the debate over the authenticity of the legendary Staff of Moses. Could either of these objects truly be the staff that parted the Red Sea and brought plagues upon Egypt?
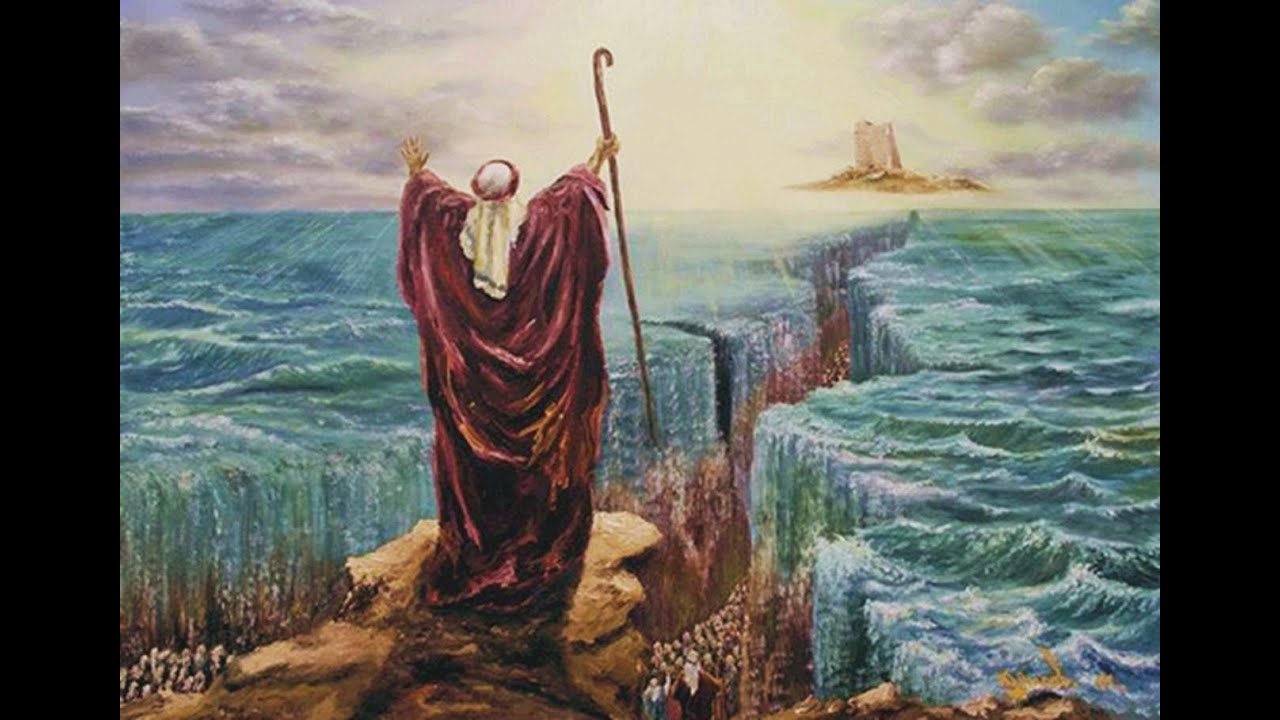

The Biblical Significance of Moses’ Staff
The Staff of Moses, also known as the Rod of God in biblical texts, is first introduced in the Book of Exodus. Initially described as a humble walking stick, the staff becomes central to Moses’ mission to free the Israelites from bondage in Egypt.
In Exodus 7, the staff is transformed into a serpent when Moses confronts Pharaoh, demonstrating divine power. Later, Moses uses it to bring about the ten plagues, beginning with turning the Nile River into blood. Its most awe-inspiring use occurs in Exodus 14, where Moses raises the staff to part the Red Sea, allowing the Israelites to escape Pharaoh’s army. When the Egyptians attempt to follow, the waters collapse upon them, sealing their doom.
These miraculous events have elevated the staff to an almost mythic status. But what became of it after Moses’ death remains a mystery, with only scattered legends offering potential clues.
The Topkapi Palace Staff
One of the most famous claims of possessing the Staff of Moses comes from the Topkapi Palace Museum in Istanbul, Turkey. This historic site, once the residence of Ottoman sultans, now displays an array of religious relics, including a wooden rod identified as Moses’ staff.
According to legend, this staff was a gift to an Ottoman sultan, passed down through centuries as a treasured artifact. The Topkapi staff is about 60 inches long and made of wood, fitting descriptions of ancient walking sticks. Visitors and some religious scholars have hailed it as the genuine Staff of Moses.
However, skeptics point to a lack of verifiable evidence. No historical documents or archaeological findings definitively trace the staff’s origins to Moses’ time. The museum’s claim rests solely on tradition, leaving its authenticity open to question.
The Birmingham Museum Staff
Another fascinating claim comes from the Birmingham Museum in England, which houses a wooden rod linked to Moses through a different set of circumstances. This staff was reportedly discovered in the mid-19th century by archaeologists excavating a tomb in Petra, a historical site in modern-day Jordan.
Petra is significant because it is believed by some to be the burial site of Moses. Beneath a monument known as the Snake Monument, the archaeologists unearthed a cave that they believed to be Moses’ tomb. Although the tomb contained no body, they found a wooden staff covered in dust and debris.
This staff, approximately four feet long, features Egyptian hieroglyphics etched in white, indicating that it belonged to a royal Egyptian court member named “Tuthmosis.” The name bears a striking resemblance to “Moses,” leading some researchers, such as author and relic hunter Graham Phillips, to believe it could indeed be the legendary staff.
Connections to Egyptian Royalty
The link between Moses and Egyptian royalty adds another layer of intrigue. According to the Bible, Moses was raised as a prince in Pharaoh’s court after being rescued from the Nile River as an infant. If Moses was indeed a member of the Egyptian royal family, it is plausible that he possessed a staff bearing hieroglyphic inscriptions.
The name “Tuthmosis,” found on the Birmingham staff, corresponds to a line of Egyptian pharaohs from the 18th dynasty. This connection has led some to theorize that Moses was an exiled Egyptian prince who adopted the Hebrew identity. However, critics argue that the name “Tuthmosis” was relatively common in ancient Egypt and may not have any direct link to Moses.
Skepticism and Lack of Evidence
Despite the allure of these artifacts, many experts remain unconvinced of their authenticity. The passage of time, coupled with the lack of verifiable provenance for both staffs, makes it nearly impossible to confirm their origins.
In the case of the Topkapi staff, there is no documented evidence connecting it to Moses beyond legend. Similarly, while the Birmingham staff’s Egyptian hieroglyphs are intriguing, they do not definitively prove a connection to the biblical figure. The 19th-century discovery of the staff in Petra also raises questions about the reliability of the excavation methods and the accuracy of the claims made by the archaeologists involved.
Symbolism and Cultural Legacy
Whether or not the Staff of Moses still exists, its significance extends far beyond the physical object. In religious and cultural traditions, the staff represents divine power, leadership, and the triumph of faith over adversity. It serves as a symbol of God’s covenant with the Israelites and His role in their liberation from slavery.
The staff’s enduring legacy is evident in art, literature, and popular culture. Depictions of Moses often include the staff, emphasizing its role in his miracles. Even modern-day relic hunters and historians continue to seek the staff, driven by its symbolic importance and the allure of uncovering a tangible link to biblical history.
Could the Staff Still Be Found?
The mystery of the Staff of Moses persists because of its disappearance from historical records. Some traditions suggest that it was passed down through the Davidic line of kings in ancient Israel, possibly used as a royal scepter. Others believe it was hidden or lost after the Babylonian conquest of Jerusalem.
Theories about its current whereabouts range from religious relic collections to undiscovered archaeological sites. However, without concrete evidence, these claims remain speculative.
Conclusion
The Staff of Moses stands at the intersection of faith, history, and legend. While the Topkapi and Birmingham staffs offer tantalizing possibilities, the lack of definitive evidence leaves the true fate of this biblical artifact shrouded in mystery.
Ultimately, the Staff of Moses is more than just a relic—it is a testament to the enduring power of stories to inspire wonder and connect us to the past. Whether it lies hidden in a museum, a tomb, or only in the pages of scripture, the staff continues to captivate believers and historians alike, reminding us of the profound impact of faith and myth on human history





